Meaning of leadership
- Leadership is defined as personal quality of an individual that influence the behavior of followers. It is an important function of management.
- Leadership is an act of influencing people so that the followers follow the path of leader.
- The successful leader must lead to stimulate and inspire the followers to achieve organizational goals.
- In an organization the manager is a leader and other subordinates are followers. A manager cannot manage effectively unless he can lead his subordinates effectively. Hence a leader may or may not be a manager but a successful manager must be a leader.
- Leadership is defined as influence, that is, the art or process of influencing people so that they will strive willingly and enthusiastically towards the achievement of group work.
Leadership style
1. Autocratic leadership style: – when the authority and decision making power are concentrated to the leader is known as autocratic leadership style. There is no participation by subordinates. The leader takes full authority and assumes full responsibility. Planning, policies and other working procedures are predetermined by the leader alone. The convey the information about what to do and how to do. He never takes any advice and suggestions of other people. They structure the entire work situation in their own way and expect the workers to follow their orders and tolerate no deviation from their order. They are just like tyrant rulers. The leader who believes and exercised the autocratic leadership style is known as autocratic leader.
Features:-
- He/she makes his own decisions and he/she doesn’t not take any advice of others because he/she thinks he/she is only superior.
- His/her position gives him/her personal authority and right to lead the members in any way he/she desires.
- Reward and punishment is exercised by him/her very strictly. Autocratic leadership style believes on negative motivational tools.
- An autocrat leader does not give full information to the members. There is only one way communication in order to maintain the position.
- An autocratic leader describes each job in detail and imposes rigid work standard on his employees. It means the subordinates are compelled to certain work assigned for him.
Advantages:-
I. It is useful in emergency or in war,
II. When the workers are undisciplined and uneducated it gives the best results.
III. When the laborers are not organized, it is more effective.
IV. There is no need of trained labor. It may be used for untrained workers.
V. It is a prompt process of decision making as the single person decides for the whole group.
Disadvantages:-
- Subordinates are not involved in the process of decision making in autocratic leadership style
- It doesn’t emphasize on correct evaluation of employee’s performance
- The moral of employees is so low.
- There is no chance of management development.
- There is no chance of two-way communication.
- Creative ideas and thinking cannot be used in autocratic leadership style.
- The employees perform the work with negative motivation.
2. Democratic leadership style: – When the authority and decision making power are decentralized to the subordinates is known as democratic leadership style. There is participation by subordinates. The leader delegates authority and provides responsibility even to the followers. Planning, policies and other working procedures are determined by the leader along with suggestions of the followers. He conveys the information about what to do and how to do just as a consultant. He takes advice and suggestions of other people. They structure the entire work situation in democratic way. They are just like democratic rulers. The leader who believes and exercised the democratic leadership style is known as democratic leader.

Features:-
- A democratic leader delegates the responsibility as per the capability of the employee
- There is participation of all subordinates in decision making
- Human values are also given preference. The leader gives concerns for the followers
- Democratic leader imposes flexible work standard, designs goals with freedom for the performance of work.
- A democratic leader emphasizes in results than on action
Advantages: –
- Good cooperation among employees is made in democratic leadership style.
- Employees are highly satisfied and their morale is increased
- Human efforts are highly recognized
- It helps in increasing in productivity.
- Policies, planning and other working procedures become better because different kinds of logic ideas and creativity are mixed.
- Subordinates have grown considerable freedom of action that helps to increase the personal growth and gets opportunity to utilize their capabilities
Disadvantages: –
- It takes long time in decision making.
- It is not suitable for untrained subordinates’
- A leader may to be responsible in his style
- It is not suitable when the followers are undisciplined and untrained
3. participative style: – when all the authority and responsibility are delegated to the subordinates is known as participative style. The leader who believes on this style is known as free rein leader. The free rein leader doesn’t use the power and leaves the power to the subordinates. He/she doesn’t provide any contribution to make planning and policies. This type of leadership style is very useful when group members are intelligent and fully aware of their roles and responsibilities.

Features
- Subordinates have complete freedom in decision making
- The subordinates are self-directed, self-motivated and self-controlled
- The role of free rein leader is to provide facilities, materials and information to the employees.
- The leader doesn’t interfere in making planning and policies
Advantages: –
- The employees are satisfied in their job because they are free in decision making
- The morale of employees is developed.
- The employees are highly developed because there is maximum possibility for the development of workers.
- The creativity and potentiality of subordinate are fully utilized.
Disadvantages:-
I. Leader contribution is ignored.
II. Sometime the subordinates are not self-directed.
III. Subordinates should not get the guidelines of the leader.
Motivation
- Motivation is an inspiration that helps to use the employees’ knowledge and skill for the growth and development of the organization.
- It is an act of persuading the people who work in the organization. It is defines as the psychological process that hell to increase the will to do work.
- It is the process of inspiring people from which the people can use their ability. It is an important function of management,.
- The employees who are engaged in the organization must be motivated.
- Without motivation, their ability and skill can’t be used properly. Every employee has the capacity to do work. It is the process that helps the employee to explore their talent.
Importance of motivation
1. Proper utilization of production factor: Motivation is the mechanism which is used to stimulate the employees. Stimulated employees are ready to use the production factor properly and efficiently. So it results in increase in production and productivity.
2. Willingness and interest creation: Motivation stimulates the employees in an organization. It influences the willingness of employees to work hard and help to present better performance. It is a process that acts according to desire of employees and increases the willingness and interest of employees to do work.
3. High productivity: When the employees are fully motivated there is better performance. It results high production and productivity increment.
4. Organizational goals:The machine, equipment, money cannot be effectively used when the employees are not motivated to do the work in an organization to the maximum extent .so it helps to achieve the organizational goals.
5. Readiness for change:Changes are required in every organization. Such changes may be in technology, environment etc. when the changes are introduced in the organization there is tendency to resist them by the employee or hesitate to accept the change. Motivated employees are already made ready to accept the change.
6. Efficiency in work:Motivated employees perform their duties according to the goals of the organization. They perform work efficiently and timely and increase the efficiency
7. Reduce absenteeism: – Motivated employees don’t want to be absent frequently. In other words, Motivated employees stay in the organization more and non Motivated employees are careless for the organizational goals.
8. Employees’ satisfaction:employee’s satisfaction is an important aspect for the managerial point of view. Employees may be motivated by fulfilling their needs and giving satisfaction in their work. In short Motivated employees are always satisfied.
9. Less disputes and strikes: disputes and strikes are harmful for organizational activities. When the employees are not motivates they are dissatisfies which creates disputes in the organization.
10. Better human relation: all employees must be treated as human beings by the organization. Motivation I mainly related to behave the human beings.
Techniques of motivation
1. Financial incentives: First techniques of motivation are financial incentives as money is indicator of success. Therefore it fulfills psychological safety and status need as people satisfy their needs by money. Wages, salary motivates employees to perform better.
2. Job enlargement: Under this technique, task assigned to do job are increased by adding simile task. So the scope of job enlargement is high for the motivation of subordinates. It is also known as horizontally leading of job.
3. Job enrichment: Under this technique jobs are made challenging and meaningful by increasing responsibility and growth opportunities. In such technique of motivation, planning and control responsibility are added to the job usually with less supervision and more self evaluation. It is also called vertical leading.
4. Job rotation: it refers to shifting an employee from one job to another. Such job rotation doesn’t mean hanging of their job but only the employees are rotated. By this it helps to develop the competency in several job which helps in development of employees.
5. Participation : Participation refers to involvement of employee in planning and decision making .it helps the employees feel that they are an asset of the organization which helps in developing ideas to solve the problems.
6. Delegation of authority:Delegation of authority is concerned with the granting of authority to the subordinates which helps in developing a feeling of dedication to work in an organization because it provides the employees high morale to perform any task.
7. Quality of work life:It is the relationship between employees’ and the total working environment of organization. It integrates employee needs and well being with improves productivity, higher job satisfaction and great employee involvement. It ensures higher level of satisfaction.
8. Management by objectives:It is used as a motivation and technique for self control of performance. By this technique superior and subordinates set goals and each individual subordinates responsibilities clearly defined which help to explore the sill and use in the organization effectively.
9. Behavior modification:The last technique of motivation is behavior modification. It develops positive motivation to the workers to do the work in desired behavior in order to modify behavior.
communication
- Communication is the process of transformation of information from one person to another. It is a process of exchanging opinions ideas, feelings, information, views and other fast between or among two or more people.
- It involves the systematic and continuous process of telling, listening and understanding. Communication skill means conveying the message to others and understanding the message from others.
- Business communication is a bridge of passing information between the management and the employees.
Process of communication
1. Source or sender: – the first step in the communication process is source or sender. The source is also called communicator. Communication begins when someone has some idea, information, view, feeling to transmit. The communicator may be a person, group or an organization. When the communicator intends to communicate to somebody communicator prepares the message
2. Encoding: – the idea or feeling the sender has to be translated into some language or symbols. This process is called encoding. The sender must choose appropriate words, symbols, pictures etc to express his/her idea.. While selecting the symbols, the sender has to pay attention about the receiver understanding the message.
3. Message or medium: – the medium is simply the pathway for transmission of the message. Some medium must be selected. This channel is chosen by the sender. They can be formal or informal. Examples are face to face , email, letters, fax. Telephone etc
4. Decoding to the receiver: – the receiver assigns some meaning to the symbol transmitted by the source, so the receiver interprets the message and the process is known as decoding. It is not an easy task because words have different meaning for different people. Problems of communication break down frequently.
5. Feedback: – this is the final phase. Feedback is the reaction of the receiver. The receiver has to confirm whether or not the message has been received or not. It is only taken in two-way communication.
6. Noise: – it is interference with the normal flow of information. It disturbs the communication system. No matter how well designed is the communication system; if noise exists the message received is different from message sent. Example: – noise of machines, vehicles, loud voice etc.
Types of communication
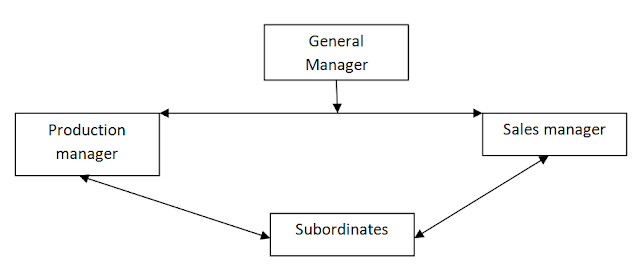
1. Horizontal communication: – it is the process of lateral flow of information in order to coordinate work activities at the same level of management hierarchy. It helps in coordination of task, share information and minimize the conflict. In other words, it is the flow of information between the activities and to solve the organization problems, this can be shown by following figure.
2. Vertical communication: – it is the process of upward and downward flow of information in order to coordinate work activities at the different level of management hierarchy. It helps in task directives, share information about rules and regulations, responsibility, problem, achievement and suggestions and minimize the conflict between subordinates and superior. There are two types of vertical communication
I. Downward communication: – it is the flow of information from top to bottom through formal lines of authority. Top level management transmits the information to subordinates about objectives, policies, strategies and responsibility.
II. Upward communication: – it is the flow of information from bottom to top in an organization. Middle and low level management transmits the information to superior about problems, suggestions
3. Diagonal communication: – it is the flow information between the superior and subordinates who are neither in the same department nor at the same level. It violates the principle of chain of command and unity of command.
Barriers to effective communication
A. Physical barriers
Internal structure of the organization and layout of office machines and equipments creates physical barriers in communication
a. Distance: – communication is found obstructed in long distance. Like communication between America and Nepal.
b. Noise: – it is from external sources and affects the communication process. Noise negatively affects the accuracy
c. Physical arrangement: – the physical arrangement of organizational sources like men, money, material and machine obstruct the communication process.
B. Semantic barriers
The use of difficult and multiple use of languages, words, figures, symbols create semantic barriers.
a. Language: – we can find some words having different meaning. As meaning sent by the sender can be quite different from the meaning understood by the receiver. Long and complex sentences creates problem in communication process.
b. Jargons: – technical or unfamiliar language creates barriers to communication that may be drawn from the literature. So message should be simple and condensed as far as possible so that no confusion creation will be there to the receiver.
C. Organizational barriers
It is raised from the organizational goals, regulations, structure and culture.
a. Poor planning: – it refers to the designing, encoding, channel selection and conflicting signals in the organization.
b. Structure complexities:- difficult organizational structure barrier for free flow of information. Appropriate communication process must be used.
c. Status differences: – it creates barrier for communication. Superior provides information to the subordinate about plans and policies. Different information is provided by different subordinates who create barrier in communication.
d. Organizational distance:- distance between sender and receiver also creates barriers to effective communication.
e. Information overload: – if superior provides too much information to the subordinate in short period receiver suffers from information overload which creates barriers to effective communication.
f. Timing: – communication can be obstructed if not done on time. If the information is not provided in time it creates barriers to effective communication.
D. Psychological barriers
It is the barriers to effective communication created from the lack of interest of the people from whom the communication is meant. People do not pay attention to the communication which are not interesting to them and which do not fulfill their want.
a. Perception: – it is the process of accepting and interpreting the information by the receiver. People receive things differently for a various number of reasons.
b. Filtering: – communication some time filters the negative information to make it more favorable to the receiver. In this process, knowingly or unknowingly some valuable information may be disposed.
c. Distrust: – superior provides information or message to the subordinates to their own view, ideas and opinion which create obstruction in communication.
d. Emotions: – emotion also creates barriers to effective communication like anger, het, mistrust, jealousy etc.
e. Viewpoint: – it also creates barriers to effective communication. It the receiver doesn’t clear the message and ignore without hearing, the message may create obstructions.
f. Defensiveness: – if the receiver receives the message as threat and interprets that message in the same way, it creates barriers to effective communication.