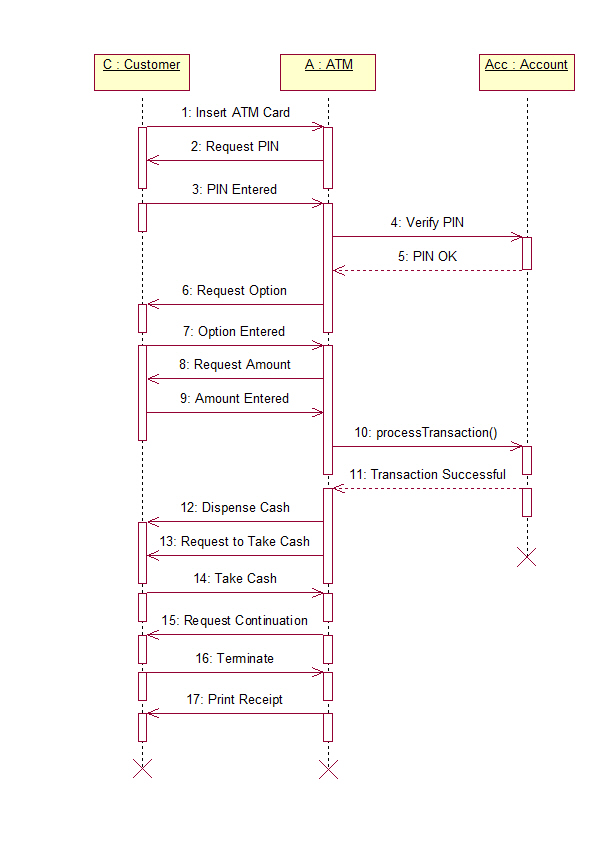
Test case for checking the login functionality of an airline seat reservation system:
Test Case Title: Check Login Functionality
Test Case ID: AIRLINE-001
Test Objective: To verify that the login functionality of the airline seat reservation system works correctly.
Preconditions:
- The user must have valid login credentials.
- The system is operational.
Test Steps:
- Enter valid login credentials (username and password).
- Click on the “Login” button.
- Verify that the system redirects the user to the homepage/dashboard after successful login.
- Verify that the user’s name or profile information is displayed on the homepage/dashboard.
- Verify that the “Logout” option is available on the homepage/dashboard.
- Logout of the system.
- Verify that the system redirects the user to the login page after logging out.
Expected Results:
– S The system successfully logs in the user and redirects them to the homepage/dashboard.
– The user’s name or profile information is displayed on the homepage/dashboard.
– The “Logout” option is available on the homepage/dashboard.
– The system successfully logs out the user and redirects them to the login page.
2021
Sure, here are examples of functional and non-functional requirements for an airline seat reservation system:
Functional Requirements:
- User Registration:
– Users should be able to register for an account with the system, providing necessary personal information.
– Upon successful registration, users should receive a confirmation email.
- Flight Search and Booking:
– Users should be able to search for flights based on criteria such as destination, departure date, and number of passengers.
– The system should display available flights matching the search criteria.
– Users should be able to select a flight and book seats for themselves and accompanying passengers.
- Seat Selection:
– Users should be able to view a seat map for each flight and select available seats.
– The system should prevent overbooking by updating seat availability in real-time.
- Payment Processing:
– Users should be able to securely enter payment information and complete transactions.
– The system should support multiple payment methods such as credit/debit cards, PayPal, etc.
- Booking Management:
– Users should have access to a dashboard where they can view and manage their bookings.
– They should be able to cancel or modify bookings within a specified time frame, with applicable fees if necessary.
- Admin Management:
– Administrators should have access to a backend interface to manage flights, seat availability, user accounts, and bookings.
– Admins should be able to add or remove flights, adjust seat capacities, and view analytics related to bookings and revenue.
Non-Functional Requirements:
- Performance:
– The system should be able to handle concurrent user requests without significant degradation in performance.
– Response times for search, booking, and payment processing should be within acceptable limits (e.g., less than 3 seconds).
- Reliability:
– The system should be available 24/7, with minimal downtime for maintenance.
– It should have backup and recovery mechanisms in place to prevent data loss in case of system failures.
- Security:
– User data, including personal and payment information, should be encrypted during transmission and storage.
– The system should comply with industry standards and regulations for data protection (e.g., GDPR, PCI DSS).
- Scalability:
– The system should be able to accommodate a growing number of users and flights without significant architectural changes.
– It should scale horizontally and vertically to handle increased traffic and data volume.
- Usability:
– The user interface should be intuitive and easy to navigate, catering to users of all technical proficiency levels.
– Error messages should be descriptive and guide users towards resolving issues.
- Accessibility:
– The system should be accessible to users with disabilities, complying with accessibility standards such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines).
– It should support screen readers, keyboard navigation, and other assistive technologies.
Q.no 5